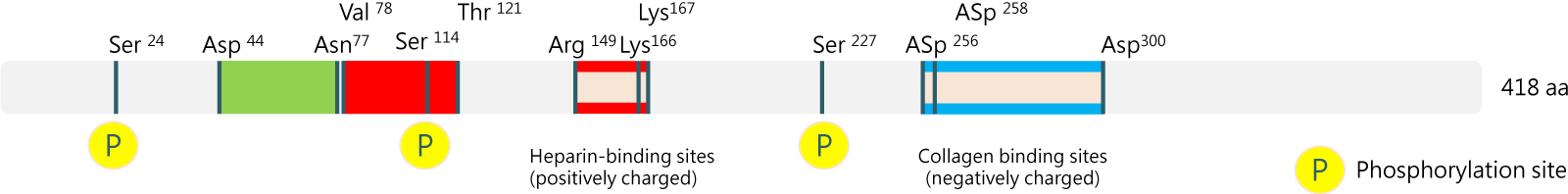
PDSP regenerative peptide technology
BRIM’s core technology platform is based on the Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF)-Derived Short Peptides, PDSP. This technology was licensed from Mackay Memorial Hospital in 2015. Within 18 months after the technology transfer, BRIM completed the preclinical development of BRM421, an innovative first-in-class therapy for dry eye disease and subsequently filed an IND application. In 2017, the US FDA approved BRM421 to initiate its first-in-human (FIH) clinical trial directly as a Phase 2 study, bypassing Phase 1. Following continuous efforts and optimization, BRIM has completed dose adjustment for BRM421 and submitted a new clinical trial application to the US FDA for a dose-ranging study. Based on the study results, the optimal dose will be selected to plan and conduct a second Phase 3 trial in the United States.
In parallel, BRIM is actively exploring PDSP applications beyond ophthalmology. Building on the achievements of its Taiwan R&D team, BRIM has established a global patent strategy to expand its innovative drug pipeline and strengthen its intellectual property portfolio. This approach not only creates value for the company but also aims to deliver high-quality, safe, effective, and affordable new therapies for patients with limited treatment options.